With 2024 now behind us, it’s clear that many of the predictions we made at the start of the year have become reality. AI’s advancements continued reshaping several industries, including game localization, and audio translation.
The impact is both at a financial and industry level. AI is reshaping workflows, jobs, and how content is produced and localized. Here, we recap some of those changes and how they impacted the translation industry.
Surge in AI Adoption and Translation Demand
2024 has witnessed an unprecedented increase in translation volumes, with a remarkable 30% year-over-year growth. Moreover, 75% of companies are planning on implementing LLMs next year. Despite this, CSA Research reports in its Q3 2024 update that the translation industry revenue has declined post-COVID until 2023. This, of course, is the after-effect of the pandemic, plus an economic crisis and uncertainty regarding the use of AI.
Despite this, revenue is forecasted to increase in the next 3 years, mainly thanks to AI-integrated tools and processes. If we follow the most neutral revenue expectations*, the language industry will go from $49.69 billion in 2023 to $55.61 in 2024 and $59.53 in 2025. However, this depends on whether the industry can adapt to the technological changes imposed by AI.
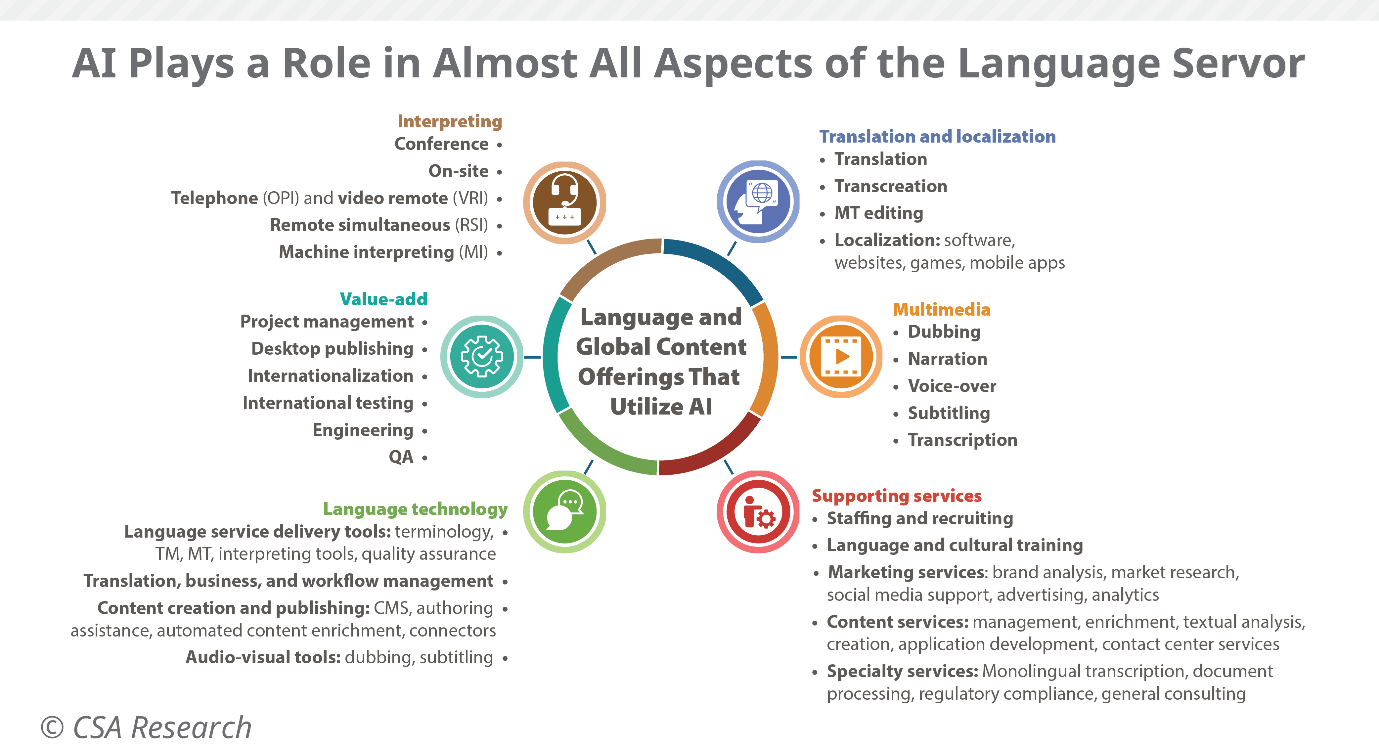
AI is already a big pillar in the language industry. The number of current tools, AI-driven services, and future developments point to future AI-powered revenues. Not only that, but AI promises to allow incursion in new markets.
*This is a projection in nominal dollars. The inflation-adjusted forecast looks slightly different and is not so optimistic since it takes revenue into account as well.
Efficiency Gains Vs Industry’s Downturn
NMT systems have improved accuracy and efficiency in translating complex texts. Real-time translation services, powered by AI, have become more reliable and contextually aware, breaking down language barriers in live communication scenarios, and creative markets.
Thanks to this, companies are reporting savings of up to 40% on per-word translation. Thus, making it possible to translate more content without incurring higher costs. This cost-effectiveness has enabled some businesses to expand their global reach and localize content for diverse markets.
Unfortunately, despite these savings, the industry was also affected by the IT and gaming crisis this year, which resulted in massive layoffs. Another factor influencing this outcome was the number of mergers and acquisitions in the localization industry this year.
The Evolution of the Traditional Translator
AI is taking on a more prominent role in the translation process. As such, the role of human translators is also undergoing a significant transformation in two ways:
- The incorporation of AI tools into localization workflows: This goes from text editors, and spell checkers to TMs and GenAI tools to check style, tone, phrasing and other stylistic resources.
- Becoming post-editors/language specialists and other MT-related jobs: Many language professionals are transitioning from traditional translation work to becoming post-editors. This means, refining and perfecting machine-generated translations. The shift requires translators to develop new skills, including proficiency in working with AI tools and an understanding of the strengths and limitations of machine translation.
The collaboration between AI and human translators is becoming more seamless. New developments allow AI to handle the bulk of straightforward translations while human experts focus on nuanced content, creative adaptation, and cultural localization.
As we mentioned in previous articles, not all is well seen and welcome: Although AI has brought numerous benefits to the translation industry, it has also raised concerns among language professionals. Some argue that this shift allows translators to specialise in different subjects. Some others say that relegating translators to post-editing becomes a “janitorial” job. What’s sure is that the role of translators is indeed changing.
A recent survey revealed that 37% of translators have incorporated generative AI into their work processes, with 8% doing so at the request of publishers or clients. This trend indicates a growing acceptance of AI tools in the translation workflow. However, it also highlights the need for translators to adapt and upskill to remain competitive in the changing landscape.
AI Integration in Translation Software
One notable development is the incorporation of NMT and GenAI into translation workflows, significantly enhancing post-editing productivity. This integration allows translators to generate alternative phrasings, adjust tone and style, and even create culturally appropriate content more efficiently.
Translation management systems have also seen substantial improvements with AI-powered features. These include automated project management, intelligent resource allocation, and predictive quality assessment tools that help streamline the entire translation process from start to finish.
These enhancements have made time and cost savings possible. However, due to the early stages of these developments, it remains to be seen how well these new workflows perform in the next year.
2024 has been the year of the AI revolution within the translation industry. From increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness to the redefinition of translators’ roles, AI has touched every aspect of the translation process.
The successful integration of AI technologies, combined with the irreplaceable human touch, positions the translation industry for a future where language barriers become increasingly surmountable. Next year, we can expect more developments in this area and more industries adopting NMT and AI translation.





